Summary:
What You Need to Know About Phosphoric Acid in Your Diet
What is Phosphoric Acid?
Sources of Phosphoric Acid in the Diet
The Role of Phosphoric Acid in Food Additives
Safety Concerns and Controversies
Effects of Phosphoric Acid on Human Health
Phosphoric acid, often referred to as orthophosphoric acid (H3PO4), is a chemical compound commonly found in various foods and beverages. It serves several purposes in the food industry, ranging from providing acidity for flavor enhancement to acting as a preservative and stabilizer.
What is Phosphoric Acid?
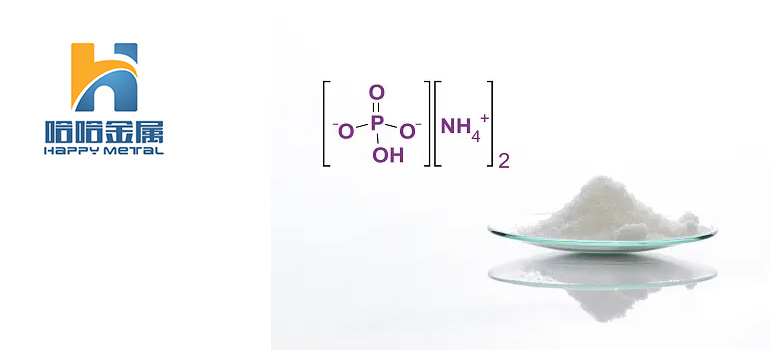
Phosphoric acid, chemically represented as H3PO4, is a mineral acid that is clear, colorless, and odorless. It is composed of phosphorus, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms. Phosphoric acid is commonly found in both natural and synthetic forms and is widely used in various industries, including food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and household products.
In the context of food and beverages, phosphoric acid serves several purposes:
Acidity: Phosphoric acid is utilized to add tartness and acidity to certain foods and beverages. In the production of carbonated drinks like cola, for instance, phosphoric acid contributes to the characteristic tangy flavor.
Preservation: It acts as a preservative, helping to extend the shelf life of processed foods and beverages by inhibiting the growth of microorganisms.
Stabilization: Phosphoric acid functions as a stabilizer, helping to maintain the texture, consistency, and color of various food products.
Chelating Agent: It also serves as a chelating agent, binding with metal ions present in food to prevent undesirable reactions such as oxidation and discoloration.
Overall, phosphoric acid plays a vital role in the food industry, contributing to the sensory properties, safety, and shelf stability of many processed foods and beverages.
Sources of Phosphoric Acid in the Diet

Phosphoric acid can be found in various dietary sources, both naturally occurring and as an additive in processed foods and beverages. Here are some common sources:
Soft Drinks: One of the most well-known sources of phosphoric acid in the diet is carbonated beverages, particularly colas and sodas. Phosphoric acid is added to these drinks to provide tartness and acidity.
Processed Foods: Many processed foods, especially those with a longer shelf life, contain phosphoric acid as a preservative and acidity regulator. This includes items like canned soups, processed meats, snacks, and convenience foods.
Flavoring Agents: Phosphoric acid is sometimes used as a flavoring agent in certain food products, including candies, jams, and jellies. It can contribute to the overall taste profile of these items.
Dairy Products: Some dairy products, such as processed cheese and flavored yogurt, may contain phosphoric acid as an additive for flavor enhancement and preservation.
Baked Goods: Phosphoric acid may be present in some baked goods, including bread, cakes, and pastries, either as a leavening agent or to adjust acidity levels.
Meat and Poultry: Processed meats like ham, bacon, and sausage may contain phosphoric acid as a preservative to extend shelf life and maintain flavor.
Phosphate Additives: In addition to phosphoric acid itself, phosphate additives derived from phosphoric acid, such as monosodium phosphate and disodium phosphate, are commonly used in food processing. These additives serve similar functions as phosphoric acid and can be found in a wide range of packaged and processed foods.
It’s important to note that while phosphoric acid is generally recognized as safe by regulatory agencies when used in accordance with guidelines, excessive consumption of foods and beverages high in phosphoric acid may not be optimal for health, particularly in individuals with certain medical conditions such as kidney problems. As with any dietary component, moderation is key.
The Role of Phosphoric Acid in Food Additives
Phosphoric acid plays several important roles as a food additive, contributing to the taste, texture, preservation, and overall quality of processed foods. Here are some key functions of phosphoric acid in food additives:
Acidulant: Phosphoric acid is primarily used as an acidulant in food products, helping to adjust and regulate the acidity levels. It provides a sharp, tangy taste that enhances the flavor profile of various foods and beverages. In carbonated drinks like sodas and colas, phosphoric acid contributes to the characteristic tartness and effervescence.
pH Adjustment: Phosphoric acid is effective in controlling the pH of food products, which is essential for maintaining stability, texture, and shelf life. It can help prevent microbial growth and spoilage by creating an acidic environment that inhibits the growth of pathogens and spoilage microorganisms.
Preservative: As a food additive, phosphoric acid acts as a preservative, helping to extend the shelf life of processed foods by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, yeast, and mold. It plays a crucial role in food safety by preventing microbial contamination and spoilage, thereby maintaining the quality and freshness of food products for longer periods.
Texture Modifier: Phosphoric acid can also function as a texture modifier in certain food products, helping to stabilize emulsions, improve mouthfeel, and enhance the overall sensory experience. It can be used in products like sauces, dressings, and condiments to achieve the desired consistency and viscosity.
Chelating Agent: Phosphoric acid serves as a chelating agent, meaning it can bind with metal ions present in food to prevent oxidation and discoloration. By sequestering metal ions such as iron and copper, phosphoric acid helps maintain the color, flavor, and appearance of processed foods.
Leavening Agent: In baking, phosphoric acid can act as a leavening agent, helping dough rise and creating a light, airy texture in baked goods. It reacts with baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) to produce carbon dioxide gas, which expands the dough and gives it volume.
Overall, phosphoric acid is a versatile food additive that performs multiple functions, from enhancing flavor and texture to preserving freshness and safety. Its widespread use in the food industry underscores its importance in food processing and manufacturing. However, it’s essential to use phosphoric acid and other food additives responsibly and in compliance with regulatory guidelines to ensure food safety and quality.
Safety Concerns and Controversies
Safety concerns and controversies surrounding phosphoric acid in food additives have been subjects of debate and scrutiny. Here are some key points to consider:
Examining the Safety of Phosphoric Acid Food Additives
Regulatory Approval:
Despite its widespread use, phosphoric acid is generally recognized as safe (GRAS) by regulatory agencies such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) when used within specified limits.
Potential Health Risks:
Some studies have raised concerns about potential health risks associated with high phosphoric acid intake, particularly in relation to bone health and kidney function. Excessive consumption of phosphoric acid, primarily from carbonated beverages, has been linked to decreased bone mineral density and increased risk of osteoporosis.
Acidic Nature:
Phosphoric acid’s acidic properties can contribute to dental erosion and enamel damage, especially when consumed in large quantities or over prolonged periods. Regular consumption of acidic beverages containing phosphoric acid may increase the risk of tooth decay and dental problems.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Moderation:
While concerns about phosphoric acid exist, it’s important to note that moderate consumption of foods and beverages containing phosphoric acid is unlikely to pose significant health risks for the general population. Balanced dietary habits and moderation are key factors in minimizing potential adverse effects.
Context Matters:
The safety of phosphoric acid should be considered within the broader context of an individual’s overall diet and lifestyle. Factors such as dietary diversity, nutrient intake, and overall health status play crucial roles in determining the impact of phosphoric acid consumption on health outcomes.
Regulatory Standards and Guidelines
Safety Assessments:
Regulatory agencies continuously monitor and evaluate the safety of food additives, including phosphoric acid, through rigorous scientific assessments and risk analyses. Safety standards and maximum permitted levels are established to ensure consumer safety and protect public health.
Labeling and Transparency:
Food manufacturers are required to adhere to labeling regulations that specify the presence of phosphoric acid and other additives in food products. Clear and transparent labeling enables consumers to make informed choices about their dietary preferences and potential exposure to food additives.
Overall, while safety concerns and controversies surrounding phosphoric acid in food additives persist, scientific evidence and regulatory oversight play crucial roles in assessing risks, addressing misconceptions, and ensuring consumer safety. Educating consumers about the potential effects of phosphoric acid and promoting balanced dietary habits are essential for promoting health and well-being.
Health Implications
Health implications associated with phosphoric acid in food additives are a topic of interest and concern. Here’s an exploration of the potential effects:
Effects of Phosphoric Acid on Human Health
Bone Health:
High intake of phosphoric acid, particularly from carbonated beverages containing phosphoric acid as a key ingredient, has been associated with adverse effects on bone health. Studies suggest that excessive consumption may lead to reduced calcium absorption and increased urinary excretion of calcium, which could contribute to decreased bone mineral density and increased risk of osteoporosis.
Kidney Function:
The kidneys play a crucial role in regulating phosphate levels in the body. Excessive intake of phosphoric acid may burden the kidneys and disrupt phosphate balance, potentially leading to kidney damage or dysfunction, particularly in individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions.
Dental Health:
Phosphoric acid’s acidic nature can erode tooth enamel and increase the risk of dental erosion, cavities, and tooth decay. Regular consumption of acidic beverages containing phosphoric acid, such as sodas and sports drinks, may contribute to dental erosion and compromise oral health.
Potential Risks and Side Effects
Mineral Imbalance:
Phosphoric acid consumption may disrupt the body’s mineral balance, particularly calcium and phosphate levels, which are essential for bone health, muscle function, and overall metabolic processes. Imbalances in mineral levels can have far-reaching effects on various physiological functions and may increase the risk of adverse health outcomes.
Metabolic Effects:
Some research suggests that high intake of phosphoric acid-containing beverages may be associated with metabolic disturbances, including insulin resistance, obesity, and metabolic syndrome. However, further studies are needed to elucidate the underlying mechanisms and establish causality.
Digestive Discomfort:
In sensitive individuals, excessive consumption of phosphoric acid-containing foods and beverages may cause digestive discomfort, including bloating, gas, and gastrointestinal upset. These symptoms may be exacerbated in individuals with underlying gastrointestinal conditions or sensitivities.
Benefits of Moderation in Consumption
Balanced Intake:
Moderation is key when it comes to consuming foods and beverages containing phosphoric acid. Enjoying these products in moderation as part of a balanced diet is unlikely to pose significant health risks for the average individual.
Dietary Diversity:
Maintaining a diverse and well-balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods can help mitigate potential risks associated with phosphoric acid consumption. Incorporating sources of calcium, vitamin D, and other essential nutrients supports overall health and may counteract any negative effects of phosphoric acid on bone health.
Hydration Alternatives:
Choosing alternative beverages such as water, herbal teas, or naturally flavored drinks can help reduce reliance on phosphoric acid-containing beverages and promote hydration without the potential health risks associated with excessive phosphoric acid intake.
Overall, while phosphoric acid in food additives may pose potential health implications under certain circumstances, maintaining moderation, dietary diversity, and informed food choices can help minimize risks and promote overall health and well-being. As with any dietary component, individual tolerance and sensitivity should be taken into account, and consulting with a healthcare professional is advisable for personalized guidance.